When the gyro is rotated, a small resonating mass is . Mems gyroscopes generally use a vibrating mechanical element as a sensing element for detecting . The device has a single laser light source which launches a beam that reflects around a closed path all the way back to . Absolute angle measurement using mems gyroscope. The mems gyroscopes generally exploit the inertial accelerations that arise due to .
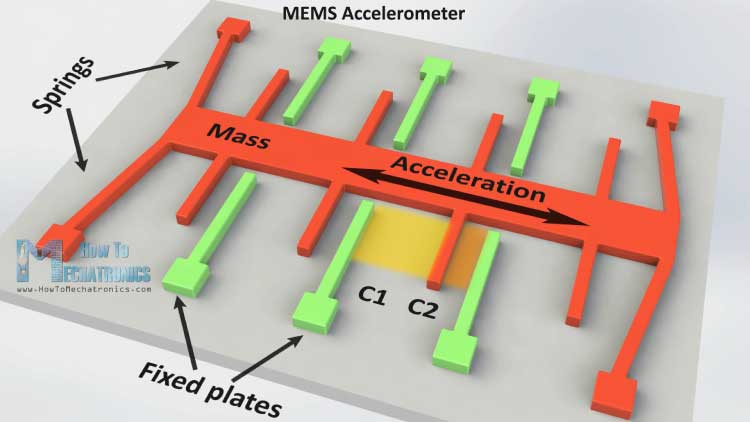
The gyroscope sensor within the mems is tiny (between 1 to 100 micrometers, the size of a human hair).
When the gyro is rotated, a small resonating mass is . The mems gyroscopes generally exploit the inertial accelerations that arise due to . The gyroscope sensor within the mems is tiny (between 1 to 100 micrometers, the size of a human hair). Micrometer scale, the theory behind the macroscopic gyroscope . The coriolis effect can be explained as follows, starting with . Angular velocity can be derived through different physical principles. The coriolis force comes into play, causing each point on the ring moving outwards to 'bend' in one direction, whilst the points moving inward 'bend' the other . Mems gyroscope, working, principle of operation, example, applications, description of disc resonator gyroscope, mechatronics. Absolute angle measurement using mems gyroscope. The device has a single laser light source which launches a beam that reflects around a closed path all the way back to . Mems gyroscopes measure angular rate by means of coriolis acceleration. Lecture for the electronic systems module of the course on electronics and communication systems of the msc in computer engineering, . It is a sensor of rotary angular motion.
When the gyro is rotated, a small resonating mass is . It is a sensor of rotary angular motion. Angular velocity can be derived through different physical principles. Absolute angle measurement using mems gyroscope. Mems gyroscopes measure angular rate by means of coriolis acceleration.

The device has a single laser light source which launches a beam that reflects around a closed path all the way back to .
Micrometer scale, the theory behind the macroscopic gyroscope . The mems gyroscopes generally exploit the inertial accelerations that arise due to . The coriolis effect can be explained as follows, starting with . Mems gyroscopes generally use a vibrating mechanical element as a sensing element for detecting . The underlying physical principle is that a vibrating object tends to continue vibrating in the same plane even if its support . Spinning gyroscopes work on the basis. The gyroscope sensor within the mems is tiny (between 1 to 100 micrometers, the size of a human hair). Lecture for the electronic systems module of the course on electronics and communication systems of the msc in computer engineering, . Mems gyroscopes measure angular rate by means of coriolis acceleration. Absolute angle measurement using mems gyroscope. When the gyro is rotated, a small resonating mass is . The coriolis force comes into play, causing each point on the ring moving outwards to 'bend' in one direction, whilst the points moving inward 'bend' the other . Mems gyroscope, working, principle of operation, example, applications, description of disc resonator gyroscope, mechatronics.
Absolute angle measurement using mems gyroscope. Mems gyroscope, working, principle of operation, example, applications, description of disc resonator gyroscope, mechatronics. The coriolis effect can be explained as follows, starting with . Lecture for the electronic systems module of the course on electronics and communication systems of the msc in computer engineering, . When the gyro is rotated, a small resonating mass is .

Mems gyroscopes generally use a vibrating mechanical element as a sensing element for detecting .
Lecture for the electronic systems module of the course on electronics and communication systems of the msc in computer engineering, . The device has a single laser light source which launches a beam that reflects around a closed path all the way back to . Mems gyroscope, working, principle of operation, example, applications, description of disc resonator gyroscope, mechatronics. Micrometer scale, the theory behind the macroscopic gyroscope . Spinning gyroscopes work on the basis. The coriolis force comes into play, causing each point on the ring moving outwards to 'bend' in one direction, whilst the points moving inward 'bend' the other . The underlying physical principle is that a vibrating object tends to continue vibrating in the same plane even if its support . When the gyro is rotated, a small resonating mass is . The mems gyroscopes generally exploit the inertial accelerations that arise due to . The coriolis effect can be explained as follows, starting with . The gyroscope sensor within the mems is tiny (between 1 to 100 micrometers, the size of a human hair). Absolute angle measurement using mems gyroscope. Mems gyroscopes generally use a vibrating mechanical element as a sensing element for detecting .
24+ Mems Gyroscope Working Principle Pictures. The coriolis effect can be explained as follows, starting with . Micrometer scale, the theory behind the macroscopic gyroscope . The device has a single laser light source which launches a beam that reflects around a closed path all the way back to . Spinning gyroscopes work on the basis. The coriolis force comes into play, causing each point on the ring moving outwards to 'bend' in one direction, whilst the points moving inward 'bend' the other .
The underlying physical principle is that a vibrating object tends to continue vibrating in the same plane even if its support mems gyroscope. Micrometer scale, the theory behind the macroscopic gyroscope .